Solution
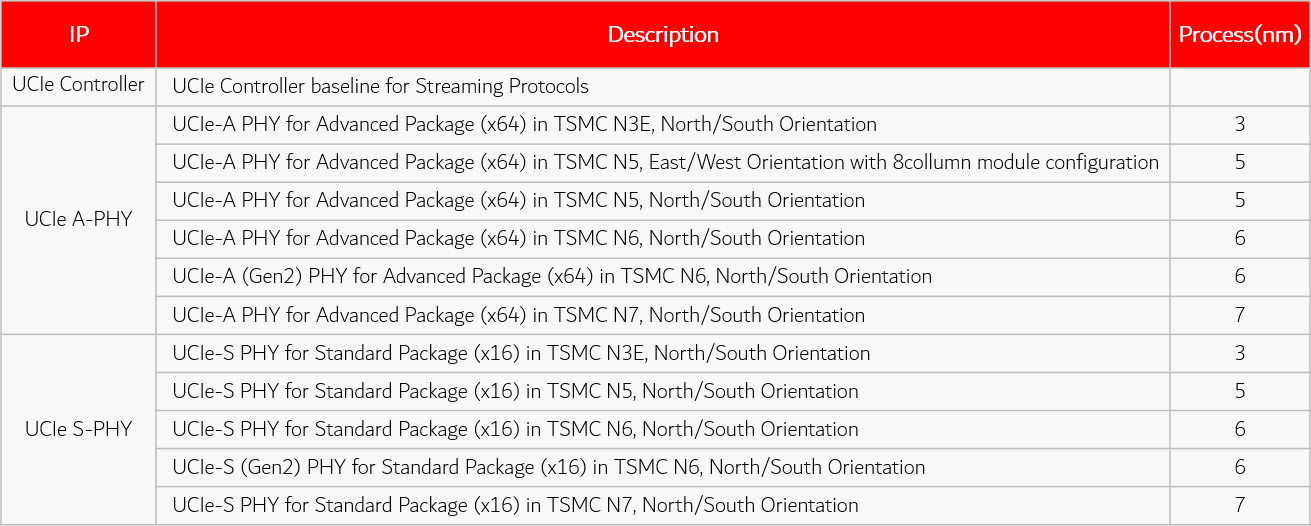
Synopsys Die-to-Die IP (UCIe)
About Die-to-Die
- Die-to-Die technology is primarily used in high-performance computing, servers, networking, and distributed AI systems, particularly for large SoC systems that approach or exceed the maximum reticle size of 800mm².
- This approach enables the scaling of SoC designs by allowing the splitting, aggregation, and disaggregation of large SoCs, and enhances modularity and flexibility while also being more cost-effective.
- By dividing functionality across several dies, it improves yield as the size of a monolithic chip nears the full reticle limit.
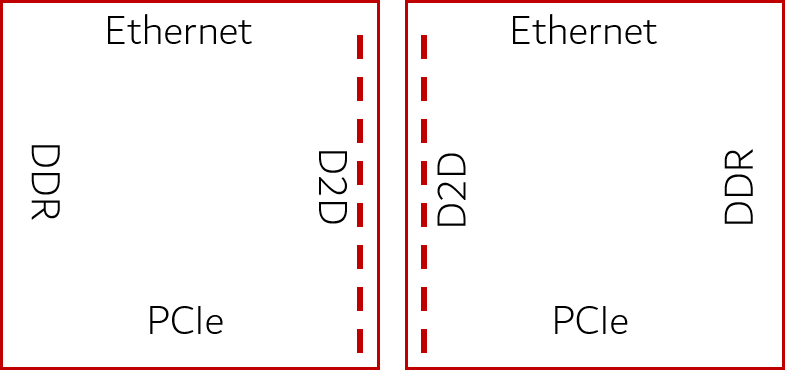
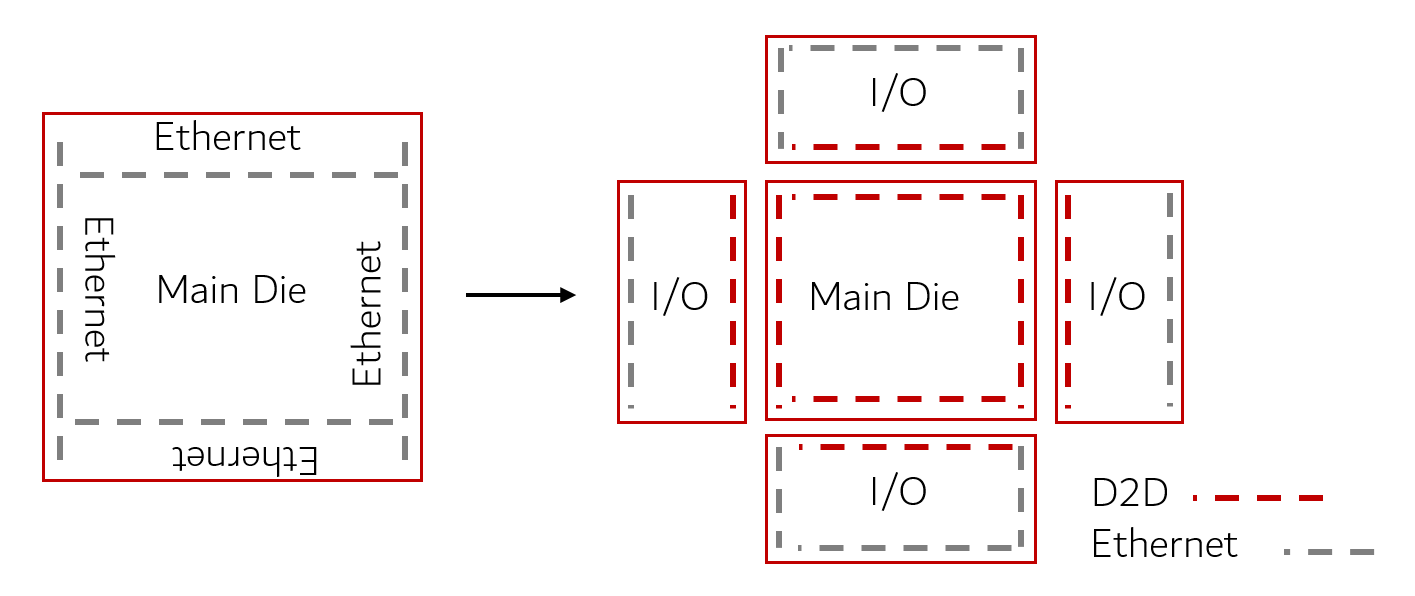
- Consider Ethernet switch SoCs as an example. These systems require data transfer rates of at least 12Tbps, or higher. To meet these demands, the SoC can be divided into a main core die surrounded by I/O dies, connected using die-to-die interconnects. This design allows for higher modularity and flexibility.
- For this configuration to be effective, the bandwidth density of the die-to-die interconnects must significantly exceed that of the SerDes in the I/O dies. This ensures that the split die arrangement operates optimally and supports the high data transfer rates needed in modern data centers.
- Utilizing die-to-die interconnect technology, contemporary chip designs are increasingly adopting solutions that integrate multiple dies within a single package.